" Black, matte and mixed skin don't need sun protection !" : another misconception about pigments. And yet, have you ever felt tightness and/or irritation as a result of sun exposure ? Or even glimpse of redness, dander, hyperpigmentation spots or an abnormally evolving mole as a result of it?
We still hear this type of cliché on black, matte and mixed skin all too often. Thanks to this article, you will understand why it is important for pigmented skin to protect itself from the sun. We will also guide you on the choice of your sun protection which must be effective to protect you properly from the harmful effects of the sun and adapted to the specificities of your skin.
Natural, scientifically proven protection
The idea that a person with pigmented skin does not need sun protection is not truthfully false.
Indeed, Fitzpatrick's classification is known internationally. It classifies the different individuals into six phototypes according to the sensitivity of their skins to the UV (ultra-violet) rays of the sun. To do this, the phototype is determined by the color of the skin according to the amount and type of melanins it possesses and the risk of melanoma developing as a result of prolonged sun exposure.
Thus, black, matte and mixed skin correspond to phototypes 4-5-6. They are characterized by dark skin, hair and eyes, and they tan easily without developing sunburn. You can determine your phototype thanks to our solar diagnosis.
On the other hand, Caucasian skins are represented by phototypes 1-2-3. They are characterized by light skin, red, blond, dark chestnut hair and eyes of green-blue and light brown color. They do not tan or lightly and easily get sunburned.
Beyond this classification, many scientific articles have statistically demonstrated that pigmented skin has a lower photo-aging and photo-carcinogenesis than fair skin. This is possible because they have a high intake of eumelanins.
Melanin : Its photoprotective role
Melanin is a biological pigment present in the epidermis of the skin. There are two types : pheomelanins (light pigments: red, yellow) and eumelanins (dark pigments : brown or black). They are both synthesized by melanocytes. Their distinction takes place during melanogenesis, depending on the enzymes involved (tyrosinase for pheomelanins and tyrosinase + TYRP 1 and 2 for eumelanins). Melanin is essential for the skin because it gives it its natural colour. Indeed, each individual has both types of melanins, but in varying quantities which induces this diversity of skin color classified according to Fitzpatrick.
Namely, physiologically, we all have the same number of melanocytes. The disparity between individuals is related to melanogenesis activity. Indeed, it is the type of pigment synthesized according to the size and the number of melanosomes that varies , so that black, matte and mixed skin has a higher level of eumelanins. It would be three to six times larger than Asian and Caucasian skins. This is genetic, their eumelanin melanosomes are larger and more numerous.
In addition, eumelanins have the particularity of having a photoprotective role. Indeed, by its biochemical characteristics, they have the ability to absorb UV radiation. They therefore limit the photo-generation of ros (free radicals) that they generate. It is these radical species that damage the skin as a result of oxidative reactions created between ROS and skin compounds (cells or fibers). Thus, they act partly as a sun filter by partially protecting the skin from the harmful effects of the sun. This is one of the reasons that scientifically explains the " black don't crack ".
Pigmented skin is deficient in vitamin D, why ?
The synthesis of vitamin D or sun hormone is carried out on the skin during sun exposure. Under the activation of UVB radiation, the 7-dehydrocholesterol present on the epidermis photolyzes into previtamin D3 which is then converted into vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
The natural protection of pigmented skin from UV rays limits the synthesis of this vitamin on the skin. They need a dose of UV rays at least six times higher than that of Caucasian skin to obtain equivalent levels of vitamin D3 in the blood. They are, therefore, people who suffer mainly from deficiency of this vitamin.
Supplementation is therefore strongly recommended by taking a dietary supplement containing vitamin D to limit the clinical signs related to this deficiency : osteoarthritis, bone and joint pain, muscle weakness, unusual fatigue, dry skin etc.
The harmful effects of the sun on black, matte and mixed skin:
We can never repeat it enough : whatever the phototype of your skin, it is essential to apply effective sun protection to protect it from the harmful effects of the sun.
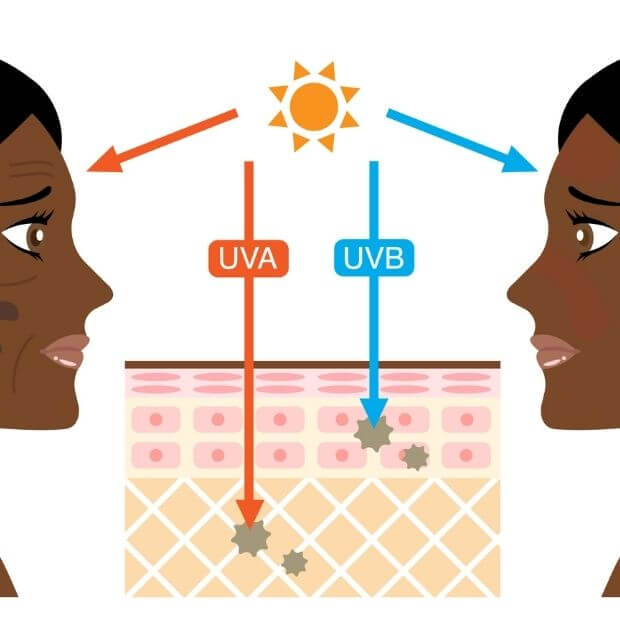
UVA, UVB which is the most dangerous ?
The sun emits invisible light containing different types of radiation depending on their wavelengths. There are three types of ultraviolet rays: UVA (400 to 315 nm), UVB (315 to 280 nm) and UVC (280 to 100nm). The latter is stopped by the ozone layer and therefore does not penetrate the skin.
- UVA : They penetrate deep into the dermis of the skin. It causes a high production of free radicals that damage the skin by creating oxidative reactions. They are thus responsible for the formation of pigment spots. They accelerate skin aging, induce skin dehydration and cause the appearance of skin cancers. (Melanomas or carcinomas).
- UVB : They penetrate the epidermis, the most superficial layers of the skin. They promote the inflammatory reaction and the creation of free radicals. They are responsible for the appearance of sunburn but they can also induce skin cancers.
Therefore, we understand that these two radiations are both harmful to the skin but that it is more important for pigmented skin to protect itself from UVA.
In addition, regarding the risk of the appearance of skin cancer, do not hesitate to regularly monitor the evolution of your moles, according to the ABCD method.
Solar hyperpigmentation spots
Tanning is a defense mechanism set up by the skin to protect itself from UV radiation from the sun. It is carried out in two simultaneous stages :
- The activation of cell proliferation in order to multiply its keratinocytes. The goal is to provide a greater mechanical barrier to limit the penetration of UV rays.
- The activation of the melanogenesis of eumelanins to benefit more from its photoprotective role. This is what makes the skin naturally in the sun darker.
However, the creation of free radicals photo-induced by UV radiation can disrupt and unbalance in excess eu-melanogenesis and thus create hyperpigmentation spots of solar origin. These are therefore caused by an overproduction of melanin and can be seen with the naked eye by the appearance on the face and / or on the body of a brown spot of darker color than the natural complexion. This is a very common phenomenon in pigmented skin.

Specific sun protection for black skin
After reading this article, you understand that despite the natural protection of black, matte and mixed skin, it is important for them to protect themselves from the harmful effects of the sun.
Including sun protection in their beauty routine must therefore be essential for them, but do we still need to know which one ? We select for you the key points that it must be able to contain to be effective while taking into account the specificities and needs of your skin.
- It must protect you from UVA and UVB in order to provide you with complete protection.
- A protection factor of 50 is ideal for the face which is very photo-exposed. On the body, an index 30 to 50 is sufficient.
- It must contain antioxidant active ingredients to eliminate free radicals created by the absorption of UV rays through the skin. This will limit their harmful effects.
The use of vitamin D3 in the formulation of cosmetic care is prohibited. Thanks to our expertise, we have been able to formulate vitamin D-like® which is an analogue of vitamin D. This helps to fight against vitamin D deficiencies that pigmented skin mainly have. Indeed, it can be accentuated by the use of sun protection that further limits the absorption of UV rays through the pigmented skin and, therefore, decreases the synthesis of this vitamin.
Zero white trace objective of sun protection on pigmented skin
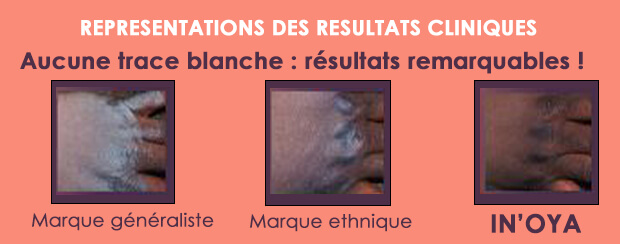
Avoid the " mask effect" or grayish complexion after applying its sun protection : this is the wish of black, matte and mixed skin.
This appears when using solar fluids composed mainly of mineral UV filters. The most commonly used molecules are zinc oxide (ZnO) and titanium dioxide (TiO2). White in color, they are able to reflect and / or disperse UV radiation so that they can not be absorbed by the skin. They thus guarantee complete protection against UVA and UVB. However, the reflected light is perceived by the retina as white. A perception more present when the skin is initially pigmented which creates this " white mask effect". In addition, the application of this type of protection requires a thick occlusive layer that can be comedogenic to the skin. This is not ideal for black, matte and mixed skin that naturally has an acne tendency.
It is therefore necessary to favor sun protection composed of organic filters. They absorb UV radiation to release heat. They are also effective on UVA and UVB and guarantee a " zero trace " effect after their applications.
How many times do I need to renew my sun protection ?
The effectiveness of the sun fluids that make up your sun protection is limited in time. This will depend on :
- The intensity of UV radiation according to location, season and time of exposure. Avoid exposing yourself between 12:00 and 16:00 because these are the hours when the intensity of UV radiation is the strongest and most dangerous.
- The amount of cream applied : the protection factor has been studied for an applied thickness of 2mg per cm². In practice, it has been noted that consumers would apply only 0.5 to 1 mg per cm².
- Friction (clothing, sand etc.) that will reduce the amount of cream applied.
- Your bathing time depending on whether the filters are soluble or not.
With regard to these factors, we recommend that you renew the application of your sun protection every 2 hours.